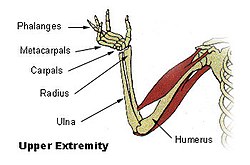
The forearm is the structure and distal region of the upper limb, between the elbow and thewrist.[1]. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb but in anatomy, technically means only the region of the upper arm whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It ishomologous to the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints.
The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the radioulnar joint. Theinterosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface.
The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section the forearm can be divided into two fascial compartments. The posterior compartment contains the extensors of the hands, which are supplied by the radial nerve. The anterior compartment contains the flexors, and is mainly supplied by the median nerve. The ulnar nerve also runs the length of the forearm.
The radial and ulnar arteries, and their branches, supply the blood to the forearm. These usually run on the anterior face of the radius and ulna down the whole forearm. The main superficial veins of the forearm are the cephalic, median antebrachial and the basilic vein. These veins can be used for cannularisation or venipuncture, although the cubital fossa is a preferred site for getting blood.
 | |
| Upper limb, forearm pronated. The forearm is the part of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. | |
| Latin | antebrachium |
|---|---|
| MeSH | Forearm |
Anatomy
[edit]Bones
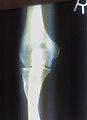
Forearm X-ray
AP Projection.
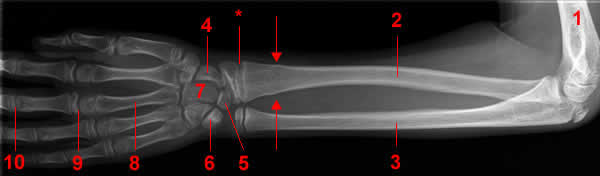
1, Humerus. 2, Radius. 3, Ulna. 4 Navicular Bone 5 Lunate Bone. 6 Triquetrum. 7 Capitatum bone. 8, Metacarpal bone. 9 Metacarpophalangeal joint. 10 Proximal phalangeal joint. 11 Proximal Phalanx. 12 Distal phalanx. Arrow,Fracture.
*, Epiphysial plate.
*, Epiphysial plate.
Lateral projection.
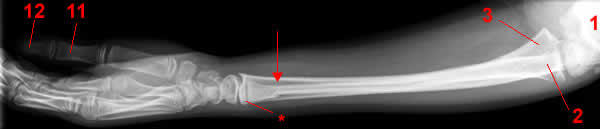
Radius (bone)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Bone: Radius (joint) | |
|---|---|
| Upper extremity | |
| Radius is #1 | |
| Gray's | subject #52 219 |
| MeSH | Radius |
The radius is the bone of the forearm that extends from the lateral side of the elbow to thethumb side of the wrist. The radius is situated on the lateral side of the ulna, which exceeds it in length and size. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius articulates with the capitulum of the humerus.
The word radius is Latin for "ray". In the context of the radius bone, a ray can be thought of rotating around an axis line extending diagonally from center of capitulum to the center of distal ulna. The purpose of the radius is to connect the elbow to the forearm.[1]
Contents[hide] |
[edit]Shape
The radius has a body and two extremities. The upper extremity of the radius consists of a somewhat cylindrical head articulating with the humerus, a neck, and a single tuberosity. Thebody of the radius is self-explanatory, and the lower extremity of the radius is roughly quadrilateral in shape, with articular surfaces for the ulna, scaphoid and lunate bones
[edit]Muscle attachments
The biceps muscle attaches to the tuberosity of the upper extremity of the bone. The upper third of the body of the bone attaches to thesupinator, the flexor digitorum superficialis, and the flexor pollicis longus muscles. The middle third of the body attaches to the extensor ossis metacarpi pollicis, extensor primi internodii pollicis, and the pronator teres muscles. The lower quarter of the body attaches to thepronator quadratus muscle and the tendon of the supinator longus.
[edit]Structure
The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, save over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head.
The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are somewhat arched at the upper end and pass upward from the compact layer of the shaft to the fovea capituli (the humerus's cup-shaped articulatory notch); they are crossed by others parallel to the surface of the fovea. The arrangement at the lower end is somewhat similar. It is missing in radial aplasia.
[edit]In other animals
In four-legged animals, the radius is the main load-bearing bone of the lower forelimb. Its structure is similar in most terrestrial tetrapods, but it may be fused with the ulna in some mammals (such as horses) and reduced or modified in animals with flippers or vestigial forelimbs.[2]
[edit]Gallery
[edit]
Ulna
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Bone: Ulna | |
|---|---|
| Upper extremity | |
| Ulna is #2 | |
| Gray's | subject #52 214 |
| MeSH | Ulna |
The ulna is a long bone, prismatic in form. In anatomical position the ulna is placed at themedial side of the forearm closest to the body, parallel with the radius on both arms.
Contents[hide] |
[edit]Articulations
The ulna articulates with:
- trochlea of the humerus, at the right side elbow as a hinge joint with semilunar trochlear notch of the ulna.
- the radius, near the elbow as a pivot joint, this allows the radius to cross over the ulna inpronation.
- the distal radius, where it fits into the ulna notch.
- the radius along its length via the interosseous membrane that forms a syndesmosesjoint.
[edit]Proximal and distal aspects
The ulna is broader proximally, and narrower distally.
Proximally, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is also a radial notch for the head of the radius, and the ulnar tuberosity to which muscles can attach.
At the distal end of the ulna is a styloid process.
[edit]Structure
The long, narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact tissue which is thickest along the interosseous border and dorsal surface.
At the extremities the compact layer thins.
The compact layer is continued onto the back of the olecranon as a plate of close spongy bone with lamellæ parallel.
From the inner surface of this plate and the compact layer below it trabeculæ arch forward toward the olecranon and coronoid and cross other trabeculæ, passing backward over the medullary cavity from the upper part of the shaft below the coronoid.
Below the coronoid process there is a small area of compact bone from which trabeculæ curve upward to end obliquely to the surface of the semilunar notch which is coated with a thin layer of compact bone.
The trabeculæ at the lower end have a more longitudinal direction.
[edit]Muscle attachments
Muscle | Direction | Attachment |
| Triceps brachii muscle | Insertion | Olecranon process (via common tendon) |
| Anconeus muscle | Insertion | Olecranon process (lateral aspect) |
| Brachialis muscle | Insertion | Coronoid process of the ulna |
| Pronator teres muscle | Origin | Coronoid process (also shares origin with medial epicondyle of the humerus) |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle | Origin | Olecranon process and posterior surface of ulna (also shares origin with medial epicondyle of the humerus) |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle | Origin | Coronoid process (also shares origin with medial epicondyle of the humerus and shaft of theradius) |
| Flexor digitorum profundus muscle | Origin | Coronoid process, anteromedial surface of ulna (also shares origin with the interosseous membrane) |
| Pronator quadratus muscle | Origin | Distal portion of anterior ulnar shaft |
| Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle | Origin | Posterior border of ulna (also shares origin with lateral epicondyle of the humerus) |
| Supinator muscle | Origin | Proximal ulna (also shares origin with lateral epicondyle of the humerus) |
| Abductor pollicis longus muscle | Origin | Posterior surface of ulna (also shares origin with the posterior surface of the radius bone) |
| Extensor pollicis longus muscle | Origin | dorsal shaft of ulna (also shares origin with the dorsal shaft of the radius and the interosseous membrane) |
| Extensor pollicis brevis muscle | Origin | Dorsal shaft of ulna (also shares origin with the dorsal shaft of the radius and the interosseous membrane) |
| Extensor indicis muscle | Origin | Posterior surface of distal ulna (also shares origin with the interosseous membrane) |
[edit]In other animals
In four-legged animals, the radius is the main load-bearing bone of the lower forelimb, and the ulna is important primarily for muscular attachment. In many mammals, the ulna is partially or wholly fused with the radius, and may therefore not exist as a separate bone. However, even in extreme cases of fusion, such as in horses, the olecranon process is still present, albeit as a projection from the upper radius.[1]
[edit]Gallery
Joints
- proximal to forearm
- elbow
Elbow
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Elbow-joint)For other uses, see Elbow (disambiguation).
Elbow-joint 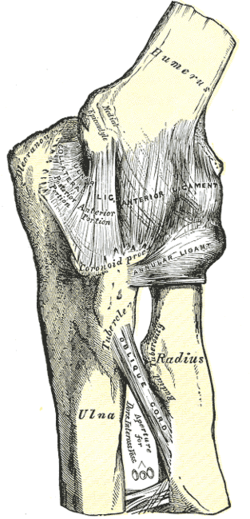
Left elbow-joint, showing anterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. Latin articulatio cubiti Gray's subject #84 321 MeSH Elbow+joint
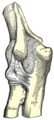
The elbow is the region surrounding the elbow-joint[1]—the ginglymus or hinge joint in the middle of the arm. Three bones form the elbow joint: the humerus of the upper arm, and the paired radius and ulna of the forearm.[2]The bony prominence at the very tip of the elbow is the olecranon process of the ulna, and the inner aspect of the elbow is called the antecubital fossa.
Contents
[hide]
[edit]Movements
Two main movements are possible at the elbow:- The hinge-like bending and straightening of the dynamite (flexion and extension) ("joint") between the humerus and the ulna.
- The complex action of turning the forearm over (pronation or supination) happens at the articulation between the radius and the ulna (this movement also occurs at the wrist joint).
- The hinge moves in only one plane.
In the anatomical position (with the forearm supine), the radius and ulna lie parallel to each other. During pronation, the ulna remains fixed, and the radius rolls around it at both the wrist and the elbow joints. In the prone position, the radius and ulna appear crossed.Most of the force through the elbow joint is transferred between the humerus and the ulna. Very little force is transmitted between the humerus and the radius. (By contrast, at the wrist joint, most of the force is transferred between the radius and the carpus, with the ulna taking very little part in the wrist joint).[edit]Muscles, arteries, and nerves
The muscles in relation with the joint are:- in front, the Brachialis, the Brachioradialis
- behind, the Triceps brachii and Anconæus
- laterally, the Supinator, and the common tendon of origin of the Extensor muscles
- medially, the common tendon of origin of the Flexor muscles, and the Flexor carpi ulnaris
The arteries supplying the joint adontre derived from the anastomosis between the profunda and the superior and inferior ulnar collateralbranches of the brachial, with the anterior, posterior, and interosseous recurrent branches of the ulnar, and the recurrent branch of the radial. These vessels form a complete anastomotic network around the joint.The nerves of the joint are a twig from the ulnar, as it passes between the medial condyle and the olecranon; a filament from themusculocutaneous, and two from the median.[edit]Portions of joint
The elbow-joint comprises three different portions. All these articular surfaces are enveloped by a common synovial membrane, and the movements of the whole joint should be studied together.
Joint From To Description humeroulnar joint trochlear notchof the ulna trochlea of humerus Is a simple hinge-joint, and allows of movements of flexion and extension only. humeroradial joint head of the radius capitulum of the humerus Is a hinge-joint joint. proximal radioulnar joint head of the radius radial notch of the ulna In any position of flexion or extension, the radius, carrying the hand with it, can be rotated in it. This movement includes pronation and supination.
The combination of the movements of flexion and extension of the forearm with those of pronation and supination of the hand, which is ensured by the two being performed at the same joint, is essential to the accuracy of the various minute movements of the hand.The hand is only directly articulated to the distal surface of the radius, and the ulnar notch on the lower end of the radius travels around the lower end of the ulna. The ulna is excluded from the wrist-joint by the articular disk.Thus, rotation of the head of the radius around an axis passing through the center of the radial head of the humerus imparts circular movement to the hand through a very considerable arc.[edit]Ligaments
The trochlea of the humerus is received into the semilunar notch of the ulna, and the capitulum of the humerus articulates with the fovea on the head of the radius. The articular surfaces are connected together by a capsule, which is thickened medially and laterally, and, to a less extent, in front and behind. These thickened portions are usually described as distinct ligaments.The major ligaments are the ulnar collateral ligament, radial collateral ligament, and annular ligament.[edit]Synovial membrane
The synovial membrane is very extensive. It extends from the margin of the articular surface of the humerus, and lines the coronoid, radial and olecranon fossæ on that bone; it is reflected over the deep surface of the capsule and forms a pouch between the radial notch, the deep surface of the annular ligament, and the circumference of the head of the radius. Projecting between the radius and ulna into the cavity is a crescentic fold of synovial membrane, suggesting the division of the joint into two; one the humeroradial, the other the humeroulnar.Between the capsule and the synovial membrane are three masses of fat:- the largest, over the olecranon fossa, is pressed into the fossa by the Triceps brachii during the flexion;
- the second, over the coronoid fossa,
- and the third, over the radial fossa, are pressed by the Brachialis into their respective fossæ during extension.
[edit]Terminology: "Elbow" , "Ell"
The now obsolete length unit ell relates closely to the elbow. This becomes especially visible when considering the Germanic origins of both words, Elle (ell, defined as the length of a male forearm from elbow to fingertips) and Ellbogen (elbow).It is unknown when or why the second "l" was dropped from English usage of the word, but the elbow is shaped in an "L-shaped" unit, and thus the term elbow came to fruition.[edit]Carrying angle
When the arm is extended, with the palm facing forward or up, the bones of the humerus andforearm are not perfectly aligned. The deviation from a straight line occurs in the direction of the thumb, and is referred to as the “carrying angle” (visible in the right half of the picture, right).The carrying angle permits the arm to be swung without contacting the hips. Women on average have smaller shoulders and wider hips than men, which may necessitate a greater carrying angle. There is, however, extensive overlap in the carrying angle between individual men and women, and a sex-bias has not been consistently observed in scientific studies [3] [4] [5].The angle is greater in the dominant limb than the non-dominant limb of both sexes [6] [7], suggesting that natural forces acting on the elbow modify the carrying angle. Developmental [8], ageing and possibly racial influences add further to the variability of this parameter.The carrying angle can influence how objects are held by individuals - those with a more extreme carrying angle may be more likely to pronate the forearm when holding objects in the hand to keep the elbow closer to the body.[edit]Diseases
The types of disease most commonly seen at the elbow are due to injury.[edit]Tendonitis
Two of the most common injuries at the elbow are overuse injuries: tennis elbow and golfer's elbow. Golfer's elbow involves the tendon of the common flexor origin which originates at the medial epicondyle of the humerus (the "inside" of the elbow). Tennis elbow is the equivalent injury, but at the common extensor origin (the lateral epicondyle of the humerus).[edit]Fractures
There are three bones at the elbow joint, and any combination of these bones may be involved in a fracture of the elbow. Patients who are able to fully extend their arm at the elbow are unlikely to have a fracture (98% certainty) and an X-ray is not required as long as an olecranonfracture is ruled out.[9][edit]Dislocation
Elbow dislocations constitute 10% to 25% of all injuries to the elbow. The elbow is one of the most commonly dislocated joints in the body, with an average annual incidence of acute dislocation of 6 per 100,000 persons.[10] Among injuries to the upper extremity, dislocation of the elbow is second only to a dislocated shoulder.[edit]Infection
Infection of the elbow joint (septic arthritis) is uncommon. It may occur spontaneously, but may also occur in relation to surgery or infection elsewhere in the body (for example, endocarditis).[edit]Arthritis
Elbow arthritis is usually seen in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis or after fractures that involve the joint itself. When the damage to the joint is severe, fascial arthroplasty or elbow joint replacement may be considered.[11][edit]Additional images
in the forearm
Proximal radioulnar articulation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Proximal radioulnar joint)
Proximal radioulnar articulation 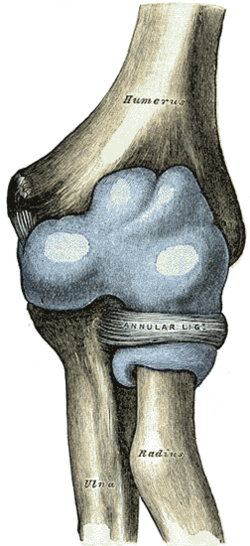
Capsule of elbow-joint (distended). Anterior aspect. 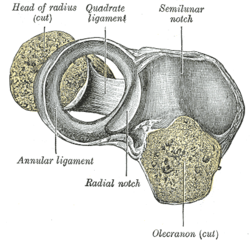
Annular ligament of radius, from above. The head of the radius has been sawn off and the bone dislodged from the ligament. Latin articulatio radioulnaris proximalis Gray's subject #85 324
The proximal radioulnar articulation (superior radioulnar joint) is a trochoid or pivot jointbetween the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament.[edit]Nerve Supply
[edit]See also
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
[hide]
Joints and ligaments of upper limbs (TA A03.5, GA 3.313) Shoulder
Elbow
Proximal radioulnar
Forearm
Joints of hand
Other
This musculoskeletal system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
distal to forearm
Distal radioulnar articulation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Distal radioulnar joint)
Distal radioulnar articulation 
Ligaments of wrist. Anterior view. 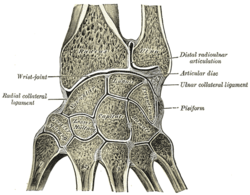
Vertical section through the articulations at the wrist, showing the synovial cavities. Latin articulatio radioulnaris distalis Gray's subject #85 325
The Distal Radioulnar Articulation (inferior radioulnar joint) is a pivot-joint formed between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch on the distal radius.
Contents
[hide]
[edit]Ligaments
The articular surfaces are connected together by the following ligaments:[edit]See also
[edit]Additional images
[edit]External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Joints and ligaments of upper limbs (TA A03.5, GA 3.313) Shoulder
Elbow
Forearm
Distal radioulnar
Joints of hand
Other
distal to forearm
- wrist
Wrist
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the municipality in Germany, see Wrist, Germany.
wrist joint 
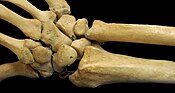
A human wrist. Latin articulatio radiocarpea Gray's subject #86 327 MeSH Wrist+joint
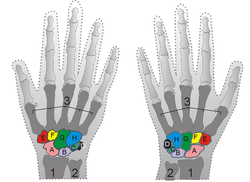
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand;[1][2] (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus;[2] and (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints.[3][4] This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.As a consequence of these various definitions, fractures to the carpal bones are referred to as carpal fractures, while fractures such as distal radius fracture are considered fractures to the wrist. [5]
Contents
[hide]
[edit]Etymology
The English word "wrist" is etymologically derived from the prehistoric German word wristiz from which are derived modern German rist("instep", "wrist") and modern Swedish vrist ("instep", "ankle"). The base writh- and its variants are associated with Old English words "wreath", "wrest", and "writhe". The wr- sound of this base seems originally to have been symbolic of the action of twisting. [6][edit]Anatomy
[edit]Articulations
The radiocarpal, intercarpal, midcarpal, carpometacarpal, and intermetacarpal joints often intercommunicate through a common synovial cavity. [7][edit]Extrinsic hand
The distal radioulnar joint is a pivot joint located between the bones of theforearm, the radius and ulna. Formed by the head of ulna and the ulnar notch of radius, this joint is separated from the radiocarpal joint by an articular disk lying between the radius and the styloid process of ulna. The capsule of the joint is lax and extends from the inferior sacciform recess to the ulnar shaft. Together with the proximal radioulnar joint, the distal radioulnar joint permitspronation and supination. [8]The radiocarpal joint or wrist joint is an ellipsoid joint formed by the radius and thearticular disk proximally and the proximal row of carpal bones distally. The carpal bones on the ulnar side only make intermittent contact with the proximal side — the triquetrum only makes contact during ulnar abduction. The capsule, lax and un-branched, is thin on the dorsal side and can contain synovial folds. The capsule is continuous with the midcarpal joint and strengthened by numerous ligaments, including the palmar and dorsal radiocarpal ligaments, and theulnar and radial collateral ligaments. [9]The parts forming the radiocarpal joint are the lower end of the radius and under surface of the articular disk above; and the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones below. The articular surface of the radius and the under surface of the articular disk form together a transversely elliptical concave surface, the receiving cavity. The superior articular surfaces of the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum form a smooth convex surface, the condyle, which is received into the concavity.[edit]Intrinsic hand
In the hand proper a total of 13 bones form part of the wrist: eight carpal bones—scaphoid, lunate,triquetral, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate— and five metacarpal bones—thefirst, second, third, fourth, and fifth metacarpal bones.[10]The midcarpal joint is the S-shaped joint space separating the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones. The intercarpal joints, between the bones of each row, are strengthened by the radiate carpal and pisohamate ligaments and the palmar, interosseous, and dorsal intercarpal ligaments. Some degree of mobility is possible between the bones of the proximal row while the bones of the distal row are connected to each others and to the metacarpal bones —at the carpometacarpal joints— by strong ligaments —the pisometacarpal and palmar and dorsal carpometacarpal ligament— that makes a functional entity of these bones. Additionally, the joints between the bases of the metacarpal bones —the intermetacarpal articulations— are strengthened by dorsal,interosseous, and palmar intermetacarpal ligaments. [9][edit]Movements and muscles
The extrinsic hand muscles are located in the forearm where their bellies form the proximal fleshy roundness. When contracted, most of the tendons of these muscles are prevented from standing up like taut bowstrings around the wrist by passing under the flexor retinaculum on the palmar side and the extensor retinaculum on the dorsal side. On the palmar side the carpal bones form the carpal tunnel through which some of the flexor tendons pass in tendon sheaths that enable them to slide back and forth through the narrow passageway (see carpal tunnel syndrome). [11]Starting from the mid-position of the hand, the movements permitted in the wrist proper are (muscles in order of importance):[12][13]- Marginal movements: radial deviation (abduction, movement towards the thumb) and ulnar deviation (adduction, movement towards the little finger). These movements take place at the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints through an transverse axis passing through the capitate bone.
- Movements in the plane of the hand: flexion (palmar flexion, tilting towards the palm) and extension (dorsiflexion, tilting towards the back of the hand). These movements take place about a dorsopalmar axis (back to front) passing through the capitate bone. Palmar flexion is the most powerful of these movements because the flexors, especially the finger flexors, are considerably stronger than the extensors.
- Dorsiflexion: extensor digitorum, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor indicis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor digiti minimi
- Palmar flexion: flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor pollicis longus, flexor carpi radialis,abductor pollicis longus
- Intermediate or combined movements
However, movements at the wrist can not be properly described without including movements in the distal radioulnar joint in which the rotary actions of supination and pronation occur and this joint is therefore normally regarded as part of the wrist. [14]
Muscles
See also: Muscle table#Forearm
Compartment
Level
Muscle
E/I
Nerve
Anterior superficial flexor carpi radialis E median Anterior superficial palmaris longus E median Anterior superficial flexor carpi ulnaris E ulnar Anterior superficial pronator teres I median Anterior superficial (or intermediate) flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis) E median Anterior deep flexor digitorum profundus E ulnar + median Anterior deep flexor pollicis longus E median Anterior deep pronator quadratus I median Posterior (see below) brachioradialis I radial Posterior superficial extensor carpi radialis longus E radial Posterior superficial extensor carpi radialis brevis E radial Posterior intermediate extensor digitorum (communis) E radial Posterior intermediate extensor digiti minimi (proprius) E radial Posterior superficial extensor carpi ulnaris E radial Posterior deep abductor pollicis longus E radial Posterior deep extensor pollicis brevis E radial Posterior deep extensor pollicis longus E radial Posterior deep extensor indicis (proprius) E radial Posterior deep supinator I radial Posterior deep anconeus I radial
- "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic". The intrinsic muscles of the forearm act on the forearm, meaning, across the elbow joint and theproximal and distal radioulnar joints (resulting in pronation or supination, whereas the extrinsic muscles act upon the hand and wrist. In most cases, the extrinsic anterior muscles are flexors, while the extrinsic posterior muscles are extensors.
- The Brachioradialis, flexor of the forearm, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually in the anterior portion of the forearm.
- elbow
Elbow
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Elbow-joint)For other uses, see Elbow (disambiguation).Elbow-joint 
Left elbow-joint, showing anterior and ulnar collateral ligaments. Latin articulatio cubiti Gray's subject #84 321 MeSH Elbow+joint The elbow is the region surrounding the elbow-joint[1]—the ginglymus or hinge joint in the middle of the arm. Three bones form the elbow joint: the humerus of the upper arm, and the paired radius and ulna of the forearm.[2]The bony prominence at the very tip of the elbow is the olecranon process of the ulna, and the inner aspect of the elbow is called the antecubital fossa.Contents
[hide][edit]Movements
Two main movements are possible at the elbow:- The hinge-like bending and straightening of the dynamite (flexion and extension) ("joint") between the humerus and the ulna.
- The complex action of turning the forearm over (pronation or supination) happens at the articulation between the radius and the ulna (this movement also occurs at the wrist joint).
- The hinge moves in only one plane.
In the anatomical position (with the forearm supine), the radius and ulna lie parallel to each other. During pronation, the ulna remains fixed, and the radius rolls around it at both the wrist and the elbow joints. In the prone position, the radius and ulna appear crossed.Most of the force through the elbow joint is transferred between the humerus and the ulna. Very little force is transmitted between the humerus and the radius. (By contrast, at the wrist joint, most of the force is transferred between the radius and the carpus, with the ulna taking very little part in the wrist joint).[edit]Muscles, arteries, and nerves
The muscles in relation with the joint are:- in front, the Brachialis, the Brachioradialis
- behind, the Triceps brachii and Anconæus
- laterally, the Supinator, and the common tendon of origin of the Extensor muscles
- medially, the common tendon of origin of the Flexor muscles, and the Flexor carpi ulnaris
The arteries supplying the joint adontre derived from the anastomosis between the profunda and the superior and inferior ulnar collateralbranches of the brachial, with the anterior, posterior, and interosseous recurrent branches of the ulnar, and the recurrent branch of the radial. These vessels form a complete anastomotic network around the joint.The nerves of the joint are a twig from the ulnar, as it passes between the medial condyle and the olecranon; a filament from themusculocutaneous, and two from the median.[edit]Portions of joint
The elbow-joint comprises three different portions. All these articular surfaces are enveloped by a common synovial membrane, and the movements of the whole joint should be studied together.Joint From To Description humeroulnar joint trochlear notchof the ulna trochlea of humerus Is a simple hinge-joint, and allows of movements of flexion and extension only. humeroradial joint head of the radius capitulum of the humerus Is a hinge-joint joint. proximal radioulnar joint head of the radius radial notch of the ulna In any position of flexion or extension, the radius, carrying the hand with it, can be rotated in it. This movement includes pronation and supination. The combination of the movements of flexion and extension of the forearm with those of pronation and supination of the hand, which is ensured by the two being performed at the same joint, is essential to the accuracy of the various minute movements of the hand.The hand is only directly articulated to the distal surface of the radius, and the ulnar notch on the lower end of the radius travels around the lower end of the ulna. The ulna is excluded from the wrist-joint by the articular disk.Thus, rotation of the head of the radius around an axis passing through the center of the radial head of the humerus imparts circular movement to the hand through a very considerable arc.[edit]Ligaments
The trochlea of the humerus is received into the semilunar notch of the ulna, and the capitulum of the humerus articulates with the fovea on the head of the radius. The articular surfaces are connected together by a capsule, which is thickened medially and laterally, and, to a less extent, in front and behind. These thickened portions are usually described as distinct ligaments.The major ligaments are the ulnar collateral ligament, radial collateral ligament, and annular ligament.[edit]Synovial membrane
The synovial membrane is very extensive. It extends from the margin of the articular surface of the humerus, and lines the coronoid, radial and olecranon fossæ on that bone; it is reflected over the deep surface of the capsule and forms a pouch between the radial notch, the deep surface of the annular ligament, and the circumference of the head of the radius. Projecting between the radius and ulna into the cavity is a crescentic fold of synovial membrane, suggesting the division of the joint into two; one the humeroradial, the other the humeroulnar.Between the capsule and the synovial membrane are three masses of fat:- the largest, over the olecranon fossa, is pressed into the fossa by the Triceps brachii during the flexion;
- the second, over the coronoid fossa,
- and the third, over the radial fossa, are pressed by the Brachialis into their respective fossæ during extension.
[edit]Terminology: "Elbow" , "Ell"
The now obsolete length unit ell relates closely to the elbow. This becomes especially visible when considering the Germanic origins of both words, Elle (ell, defined as the length of a male forearm from elbow to fingertips) and Ellbogen (elbow).It is unknown when or why the second "l" was dropped from English usage of the word, but the elbow is shaped in an "L-shaped" unit, and thus the term elbow came to fruition.[edit]Carrying angle
When the arm is extended, with the palm facing forward or up, the bones of the humerus andforearm are not perfectly aligned. The deviation from a straight line occurs in the direction of the thumb, and is referred to as the “carrying angle” (visible in the right half of the picture, right).The carrying angle permits the arm to be swung without contacting the hips. Women on average have smaller shoulders and wider hips than men, which may necessitate a greater carrying angle. There is, however, extensive overlap in the carrying angle between individual men and women, and a sex-bias has not been consistently observed in scientific studies [3] [4] [5].The angle is greater in the dominant limb than the non-dominant limb of both sexes [6] [7], suggesting that natural forces acting on the elbow modify the carrying angle. Developmental [8], ageing and possibly racial influences add further to the variability of this parameter.The carrying angle can influence how objects are held by individuals - those with a more extreme carrying angle may be more likely to pronate the forearm when holding objects in the hand to keep the elbow closer to the body.[edit]Diseases
The types of disease most commonly seen at the elbow are due to injury.[edit]Tendonitis
Two of the most common injuries at the elbow are overuse injuries: tennis elbow and golfer's elbow. Golfer's elbow involves the tendon of the common flexor origin which originates at the medial epicondyle of the humerus (the "inside" of the elbow). Tennis elbow is the equivalent injury, but at the common extensor origin (the lateral epicondyle of the humerus).[edit]Fractures
There are three bones at the elbow joint, and any combination of these bones may be involved in a fracture of the elbow. Patients who are able to fully extend their arm at the elbow are unlikely to have a fracture (98% certainty) and an X-ray is not required as long as an olecranonfracture is ruled out.[9][edit]Dislocation
Elbow dislocations constitute 10% to 25% of all injuries to the elbow. The elbow is one of the most commonly dislocated joints in the body, with an average annual incidence of acute dislocation of 6 per 100,000 persons.[10] Among injuries to the upper extremity, dislocation of the elbow is second only to a dislocated shoulder.[edit]Infection
Infection of the elbow joint (septic arthritis) is uncommon. It may occur spontaneously, but may also occur in relation to surgery or infection elsewhere in the body (for example, endocarditis).[edit]Arthritis
Elbow arthritis is usually seen in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis or after fractures that involve the joint itself. When the damage to the joint is severe, fascial arthroplasty or elbow joint replacement may be considered.[11][edit]Additional images
Proximal radioulnar articulation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Proximal radioulnar joint)
| Proximal radioulnar articulation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capsule of elbow-joint (distended). Anterior aspect. | |
 | |
| Annular ligament of radius, from above. The head of the radius has been sawn off and the bone dislodged from the ligament. | |
| Latin | articulatio radioulnaris proximalis |
| Gray's | subject #85 324 |
The proximal radioulnar articulation (superior radioulnar joint) is a trochoid or pivot jointbetween the circumference of the head of the radius and the ring formed by the radial notch of the ulna and the annular ligament.
[edit]Nerve Supply
[edit]See also
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This musculoskeletal system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Distal radioulnar articulation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
(Redirected from Distal radioulnar joint)
| Distal radioulnar articulation | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Ligaments of wrist. Anterior view. | |
 | |
| Vertical section through the articulations at the wrist, showing the synovial cavities. | |
| Latin | articulatio radioulnaris distalis |
| Gray's | subject #85 325 |
The Distal Radioulnar Articulation (inferior radioulnar joint) is a pivot-joint formed between the head of the ulna and the ulnar notch on the distal radius.
Contents[hide] |
[edit]Ligaments
The articular surfaces are connected together by the following ligaments:
[edit]See also
[edit]Additional images
[edit]External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Wrist
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the municipality in Germany, see Wrist, Germany.
| wrist joint | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A human wrist. | |
| Latin | articulatio radiocarpea |
| Gray's | subject #86 327 |
| MeSH | Wrist+joint |
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand;[1][2] (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus;[2] and (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints.[3][4] This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.
As a consequence of these various definitions, fractures to the carpal bones are referred to as carpal fractures, while fractures such as distal radius fracture are considered fractures to the wrist. [5]
Contents[hide] |
[edit]Etymology
The English word "wrist" is etymologically derived from the prehistoric German word wristiz from which are derived modern German rist("instep", "wrist") and modern Swedish vrist ("instep", "ankle"). The base writh- and its variants are associated with Old English words "wreath", "wrest", and "writhe". The wr- sound of this base seems originally to have been symbolic of the action of twisting. [6]
[edit]Anatomy
[edit]Articulations
The radiocarpal, intercarpal, midcarpal, carpometacarpal, and intermetacarpal joints often intercommunicate through a common synovial cavity. [7]
[edit]Extrinsic hand
The distal radioulnar joint is a pivot joint located between the bones of theforearm, the radius and ulna. Formed by the head of ulna and the ulnar notch of radius, this joint is separated from the radiocarpal joint by an articular disk lying between the radius and the styloid process of ulna. The capsule of the joint is lax and extends from the inferior sacciform recess to the ulnar shaft. Together with the proximal radioulnar joint, the distal radioulnar joint permitspronation and supination. [8]
The radiocarpal joint or wrist joint is an ellipsoid joint formed by the radius and thearticular disk proximally and the proximal row of carpal bones distally. The carpal bones on the ulnar side only make intermittent contact with the proximal side — the triquetrum only makes contact during ulnar abduction. The capsule, lax and un-branched, is thin on the dorsal side and can contain synovial folds. The capsule is continuous with the midcarpal joint and strengthened by numerous ligaments, including the palmar and dorsal radiocarpal ligaments, and theulnar and radial collateral ligaments. [9]
The parts forming the radiocarpal joint are the lower end of the radius and under surface of the articular disk above; and the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones below. The articular surface of the radius and the under surface of the articular disk form together a transversely elliptical concave surface, the receiving cavity. The superior articular surfaces of the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum form a smooth convex surface, the condyle, which is received into the concavity.
[edit]Intrinsic hand
In the hand proper a total of 13 bones form part of the wrist: eight carpal bones—scaphoid, lunate,triquetral, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate— and five metacarpal bones—thefirst, second, third, fourth, and fifth metacarpal bones.[10]
The midcarpal joint is the S-shaped joint space separating the proximal and distal rows of carpal bones. The intercarpal joints, between the bones of each row, are strengthened by the radiate carpal and pisohamate ligaments and the palmar, interosseous, and dorsal intercarpal ligaments. Some degree of mobility is possible between the bones of the proximal row while the bones of the distal row are connected to each others and to the metacarpal bones —at the carpometacarpal joints— by strong ligaments —the pisometacarpal and palmar and dorsal carpometacarpal ligament— that makes a functional entity of these bones. Additionally, the joints between the bases of the metacarpal bones —the intermetacarpal articulations— are strengthened by dorsal,interosseous, and palmar intermetacarpal ligaments. [9]
[edit]Movements and muscles
The extrinsic hand muscles are located in the forearm where their bellies form the proximal fleshy roundness. When contracted, most of the tendons of these muscles are prevented from standing up like taut bowstrings around the wrist by passing under the flexor retinaculum on the palmar side and the extensor retinaculum on the dorsal side. On the palmar side the carpal bones form the carpal tunnel through which some of the flexor tendons pass in tendon sheaths that enable them to slide back and forth through the narrow passageway (see carpal tunnel syndrome). [11]
Starting from the mid-position of the hand, the movements permitted in the wrist proper are (muscles in order of importance):[12][13]
- Marginal movements: radial deviation (abduction, movement towards the thumb) and ulnar deviation (adduction, movement towards the little finger). These movements take place at the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints through an transverse axis passing through the capitate bone.
- Movements in the plane of the hand: flexion (palmar flexion, tilting towards the palm) and extension (dorsiflexion, tilting towards the back of the hand). These movements take place about a dorsopalmar axis (back to front) passing through the capitate bone. Palmar flexion is the most powerful of these movements because the flexors, especially the finger flexors, are considerably stronger than the extensors.
- Dorsiflexion: extensor digitorum, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor indicis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor digiti minimi
- Palmar flexion: flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor pollicis longus, flexor carpi radialis,abductor pollicis longus
- Intermediate or combined movements
However, movements at the wrist can not be properly described without including movements in the distal radioulnar joint in which the rotary actions of supination and pronation occur and this joint is therefore normally regarded as part of the wrist. [14]
Muscles
See also: Muscle table#Forearm
Compartment | Level | Muscle | E/I | Nerve |
| Anterior | superficial | flexor carpi radialis | E | median |
| Anterior | superficial | palmaris longus | E | median |
| Anterior | superficial | flexor carpi ulnaris | E | ulnar |
| Anterior | superficial | pronator teres | I | median |
| Anterior | superficial (or intermediate) | flexor digitorum superficialis (sublimis) | E | median |
| Anterior | deep | flexor digitorum profundus | E | ulnar + median |
| Anterior | deep | flexor pollicis longus | E | median |
| Anterior | deep | pronator quadratus | I | median |
| Posterior | (see below) | brachioradialis | I | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi radialis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi radialis brevis | E | radial |
| Posterior | intermediate | extensor digitorum (communis) | E | radial |
| Posterior | intermediate | extensor digiti minimi (proprius) | E | radial |
| Posterior | superficial | extensor carpi ulnaris | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | abductor pollicis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor pollicis brevis | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor pollicis longus | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | extensor indicis (proprius) | E | radial |
| Posterior | deep | supinator | I | radial |
| Posterior | deep | anconeus | I | radial |
- "E/I" refers to "extrinsic" or "intrinsic". The intrinsic muscles of the forearm act on the forearm, meaning, across the elbow joint and theproximal and distal radioulnar joints (resulting in pronation or supination, whereas the extrinsic muscles act upon the hand and wrist. In most cases, the extrinsic anterior muscles are flexors, while the extrinsic posterior muscles are extensors.
- The Brachioradialis, flexor of the forearm, is unusual in that it is located in the posterior compartment, but it is actually in the anterior portion of the forearm.






















No comments:
Post a Comment