 |
 |  |  |  |
|
|
 |  |
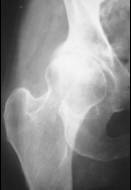
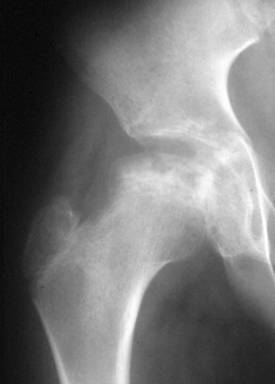
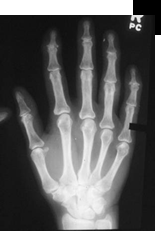
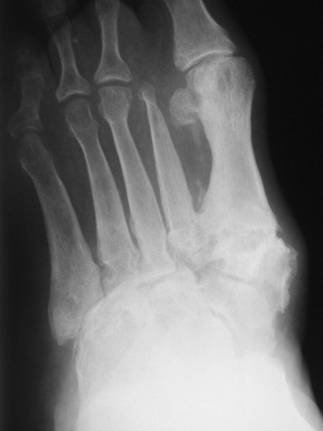
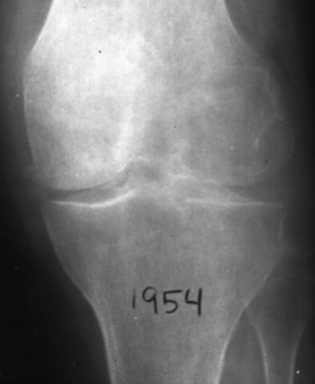
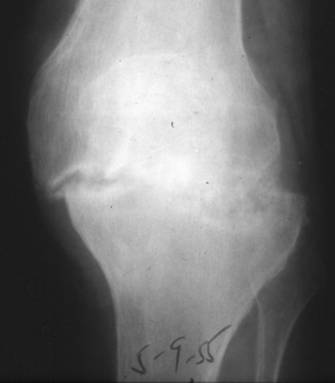
| Calcium Pyrophosphate | |
| Deposition Disease (CPPD) |
| |
|
|
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| n | May be idiopathic or associated with | |
|
| l | Hyperparathyroidism, hemochromatosis |
|
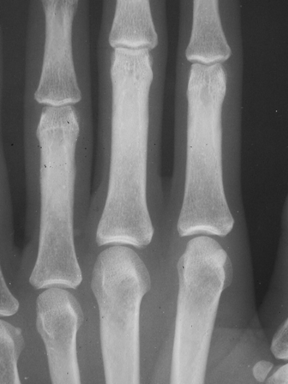
| n | Symmetric involvement: knees (most |
|
| common), wrists, MCPs | |
|
| n | Sudden onset of pain and fever | |
|
| n | Clinically | |
|
| l | Tender, swollen, red, LOM |
|
 |  |  |












No comments:
Post a Comment